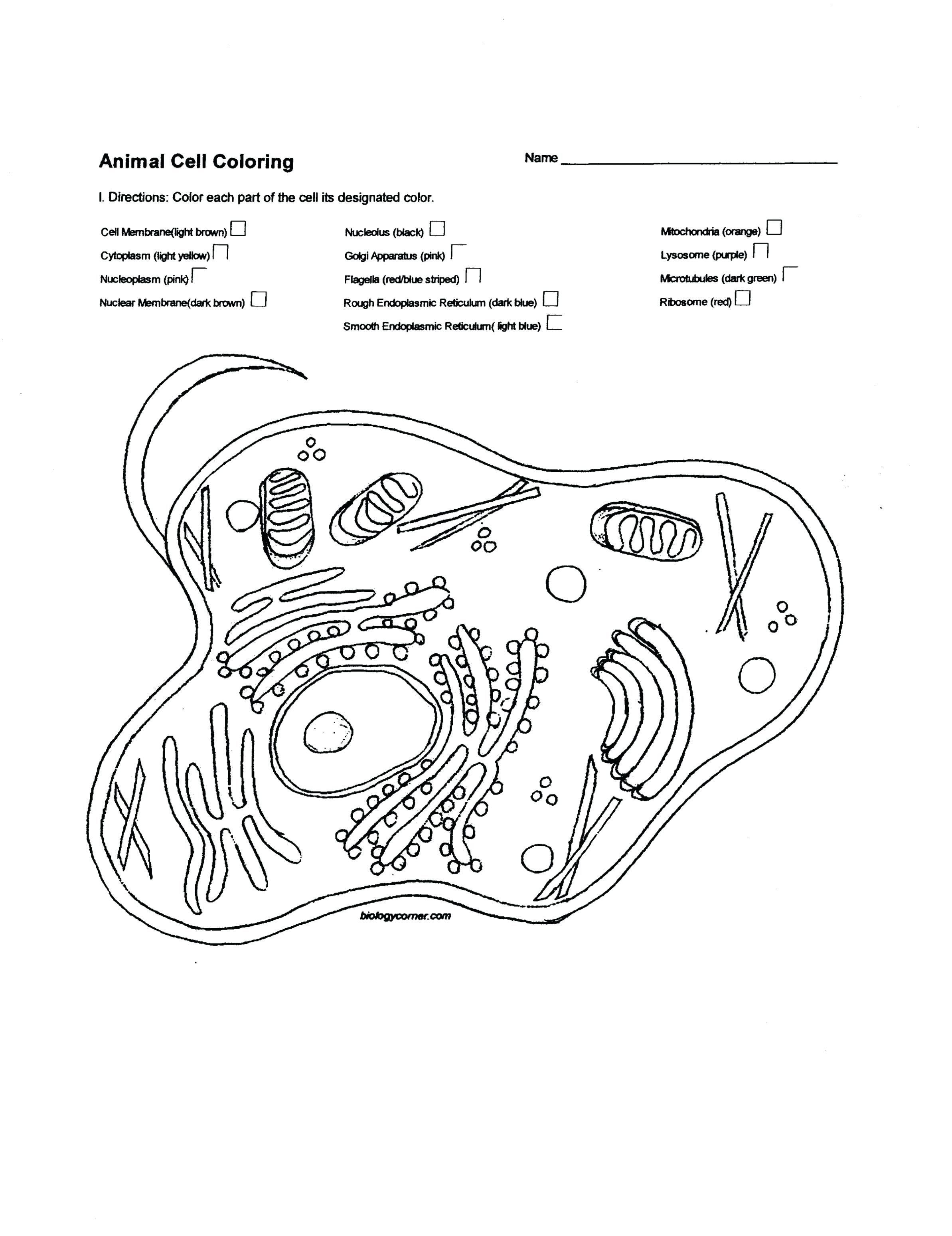
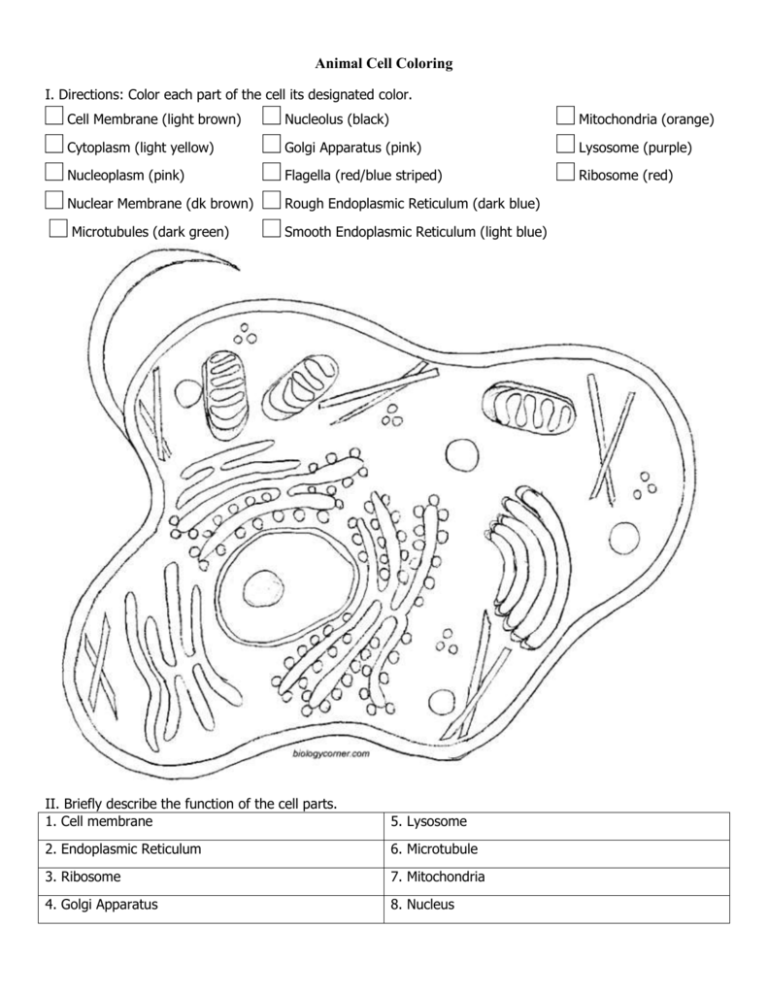
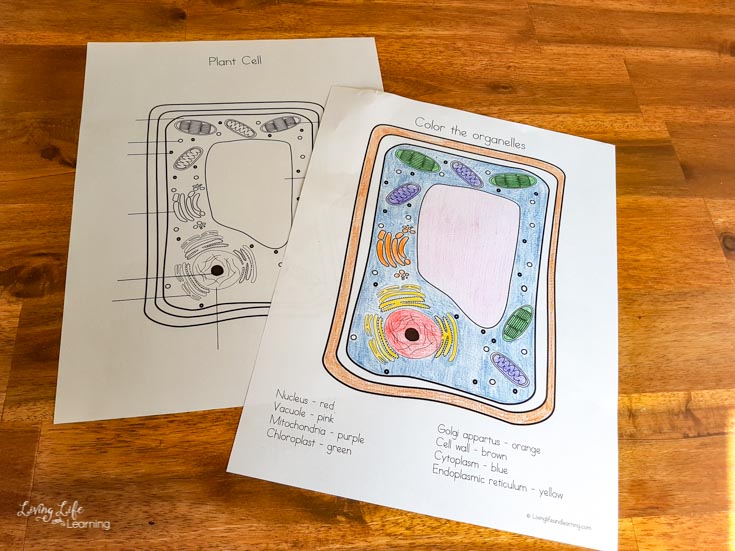
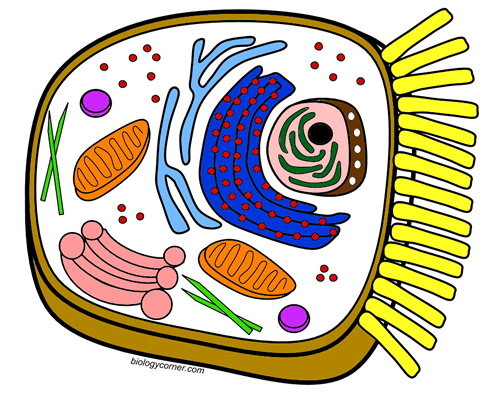
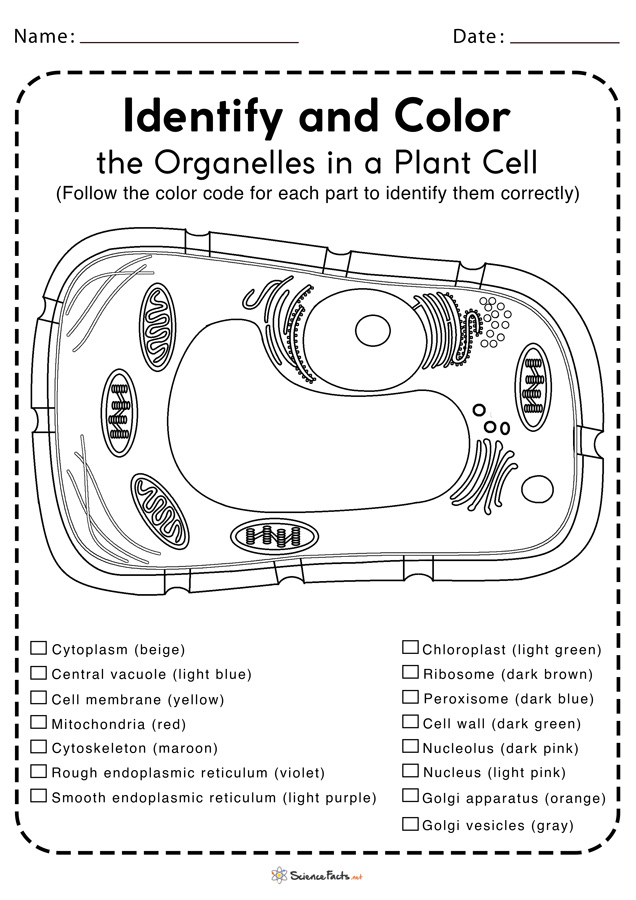
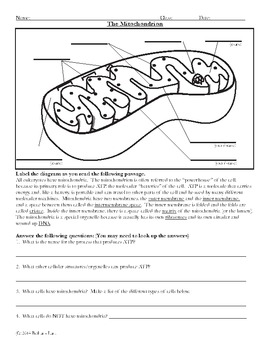
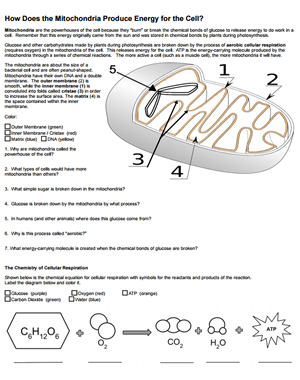
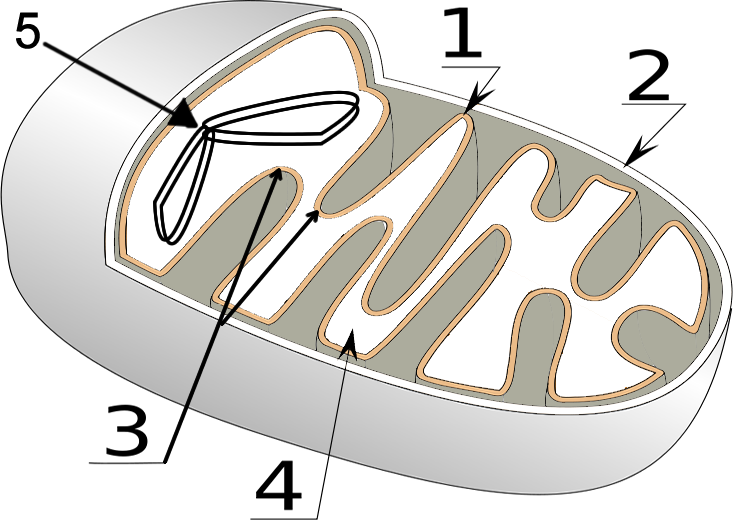
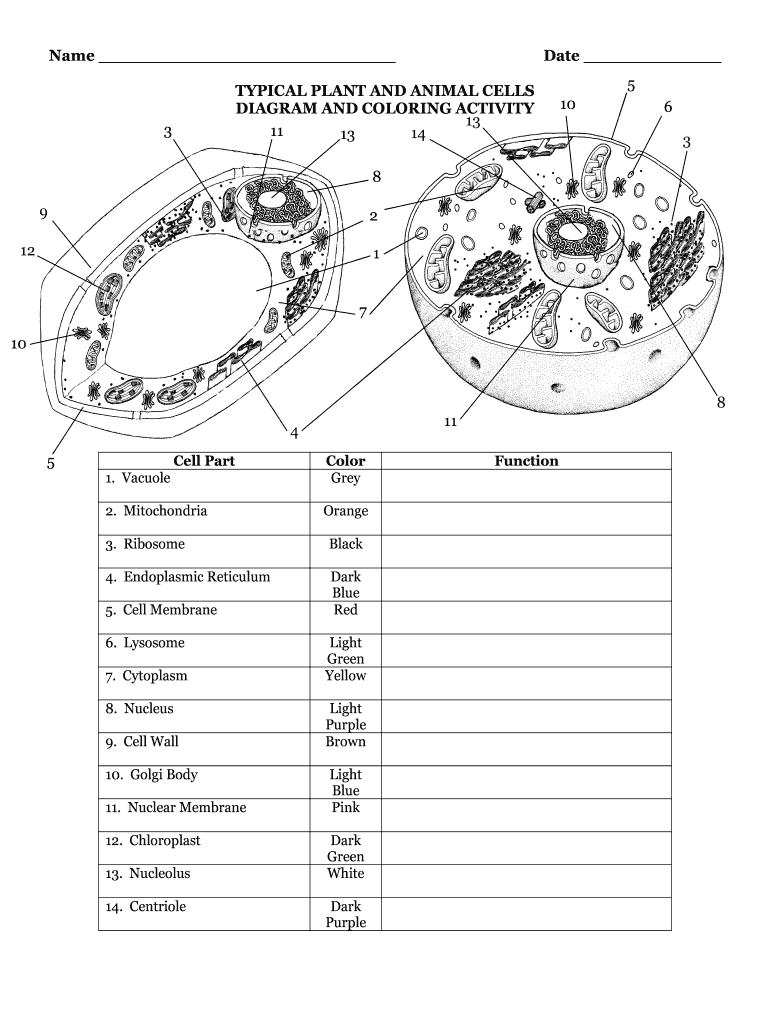
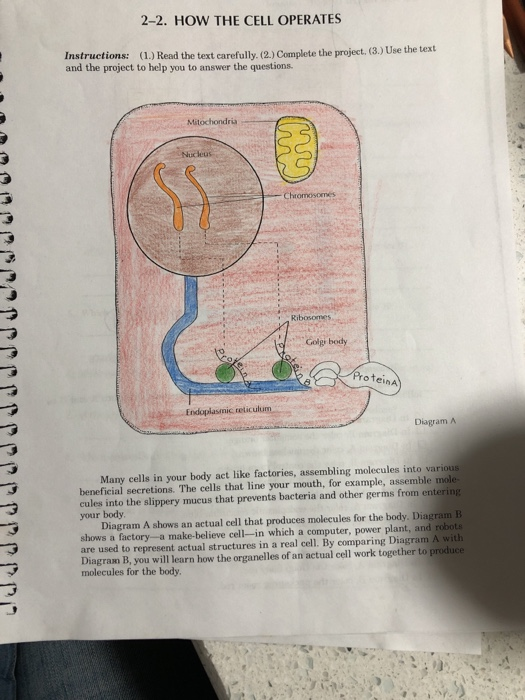
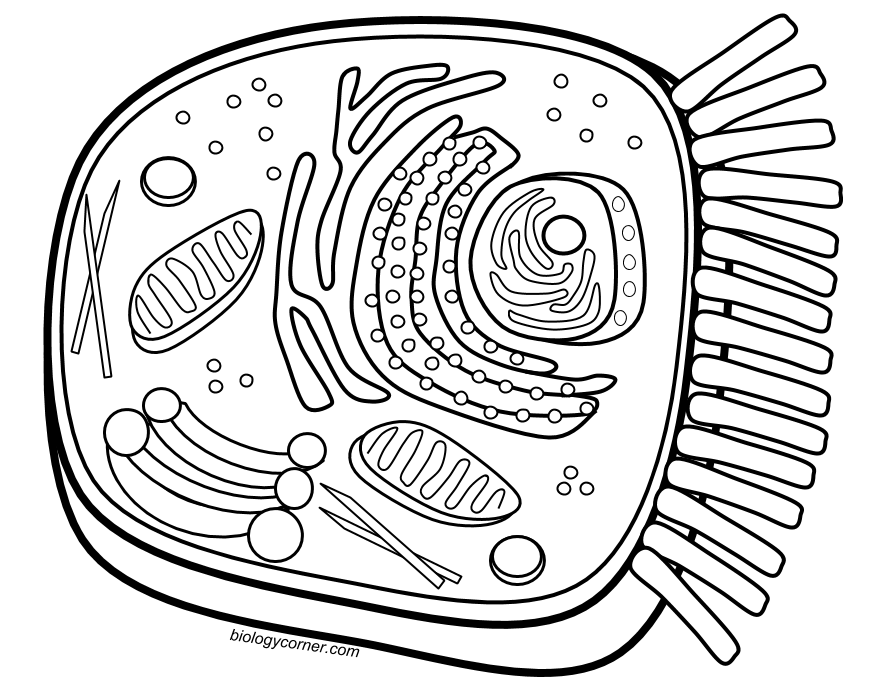
41 mitochondria coloring worksheet answer key
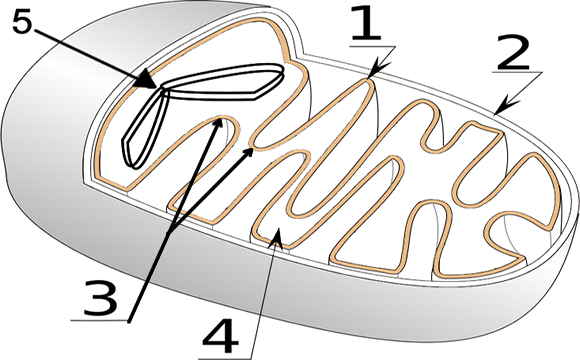
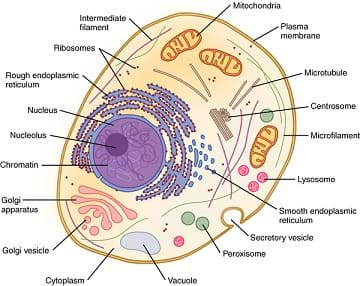
Mitochondrion - Wikipedia A mitochondrion ( / ˌmaɪtəˈkɒndriən /; [1] pl. mitochondria) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. [2] What Is Mitochondria (Structure, Diagram & Function) - BYJUS Mitochondria are the cell organelles that are responsible for producing ATP, the energy currency of the cell. 3. Briefly describe the structure of mitochondria. Mitochondria is a rod-shaped, double membraned organelle. It is found both in plant cells and animal cells. 4. What are cristae? The inner membrane of mitochondria has many folds.
The Mitochondria 2023 Jan 15, 2023 · The International Symposium on “Mitochondria, Cell Death and Human Diseases” is being organized by the School of Life Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), New Delhi, India in association with Rutgers School of Biomedical and Health Sciences, USA, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, USA and Cancer Research and Care Academy, New Delhi on …

Mitochondria coloring worksheet answer key
Mitochondrial Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment Mitochondria are the “energy factory” of our body. Mitochondrial diseases are long-term, genetic, often inherited disorders that occur when mitochondria fail to produce enough energy for the body to function properly. One in 5,000 individuals has a genetic mitochondrial disease. Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment are discussed. Appointments & Access Mitochondria - Genome.gov Jan 12, 2023 · Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. Chemical energy produced by the mitochondria is stored in a small molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondria contain their own small chromosomes. Mitochondrion | Definition, Function, Structure, & Facts Jan 5, 2023 · Mitochondria are found in the cells of nearly every eukaryotic organism, including plants and animals. Cells that require a lot of energy, such as muscle cells, can contain hundreds or thousands of mitochondria. A few types of cells, such as red blood cells, lack mitochondria entirely. As prokaryotic organisms, bacteria and archaea do not have mitochondria.
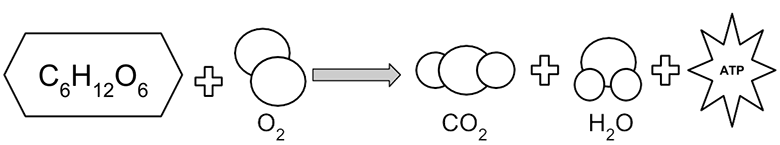
Mitochondria coloring worksheet answer key. Mitochondria: Form, function, and disease - Medical News Today Feb 8, 2018 · Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. They help turn the energy we take from food into energy that the cell can use. But, there is more to mitochondria than energy... Mitochondria - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Mitochondria play a critical role in the generation of metabolic energy in eukaryotic cells. As reviewed in Chapter 2, they are responsible for most of the useful energy derived from the breakdown of carbohydrates and fatty acids, which is converted to ATP by the process of oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondrion - Wikipedia A mitochondrion (/ ˌ m aɪ t ə ˈ k ɒ n d r i ə n /; pl. mitochondria) is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. Mitochondria: 10 Ways to Boost the Powerhouse of Your Cells Jul 1, 2019 · Mitochondria sustain human life because they generate the energy that powers our cells. By supporting mitochondrial fitness, we are supporting the optimal functioning of pretty much every cell and system in our body. Boosting mitochondria can help us live a long and healthy life.
Mitochondria - Definition, Function & Structure | Biology Dictionary Mar 3, 2017 · Definition. Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) are organelles within eukaryotic cells that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy molecule used by the cell. For this reason, the mitochondrion is sometimes referred to as “the powerhouse of the cell”. Mitochondria are found in all eukaryotes, which are all living things that are not bacteria or archaea. Mitochondrial DNA - Genome.gov Jan 12, 2023 · Mitochondria are organelles that produce ATP, which is the major source of energy for our cells. People who like endurance sports, like I do, think about mitochondria a lot, because a lot of what you're doing when you're training is getting your cells to make more mitochondria so that your muscles are able to cope with the demand you put on them. Mitochondrion | Definition, Function, Structure, & Facts Jan 5, 2023 · Mitochondria are found in the cells of nearly every eukaryotic organism, including plants and animals. Cells that require a lot of energy, such as muscle cells, can contain hundreds or thousands of mitochondria. A few types of cells, such as red blood cells, lack mitochondria entirely. As prokaryotic organisms, bacteria and archaea do not have mitochondria. Mitochondria - Genome.gov Jan 12, 2023 · Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. Chemical energy produced by the mitochondria is stored in a small molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondria contain their own small chromosomes.
Mitochondrial Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment Mitochondria are the “energy factory” of our body. Mitochondrial diseases are long-term, genetic, often inherited disorders that occur when mitochondria fail to produce enough energy for the body to function properly. One in 5,000 individuals has a genetic mitochondrial disease. Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment are discussed. Appointments & Access





















Komentar
Posting Komentar