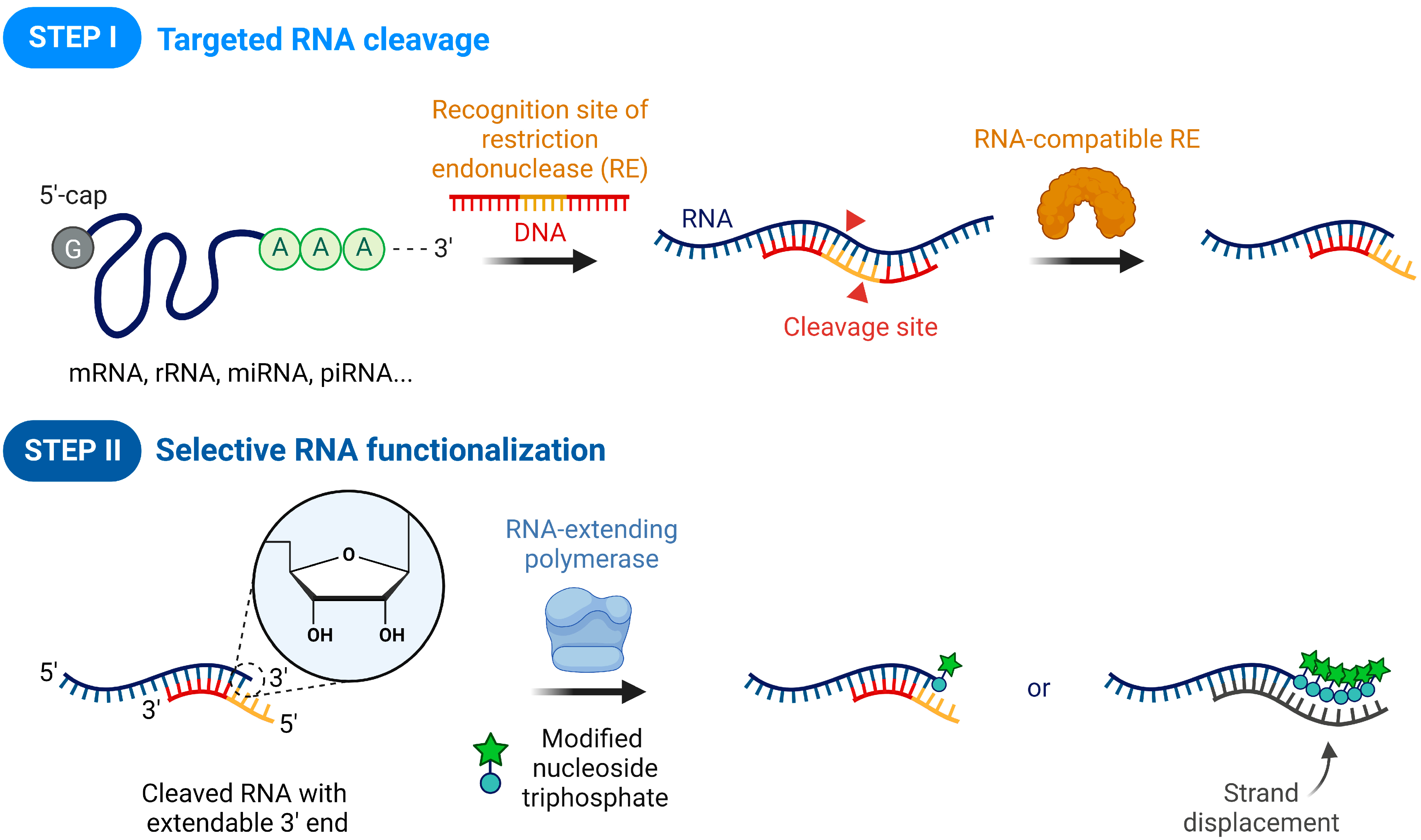
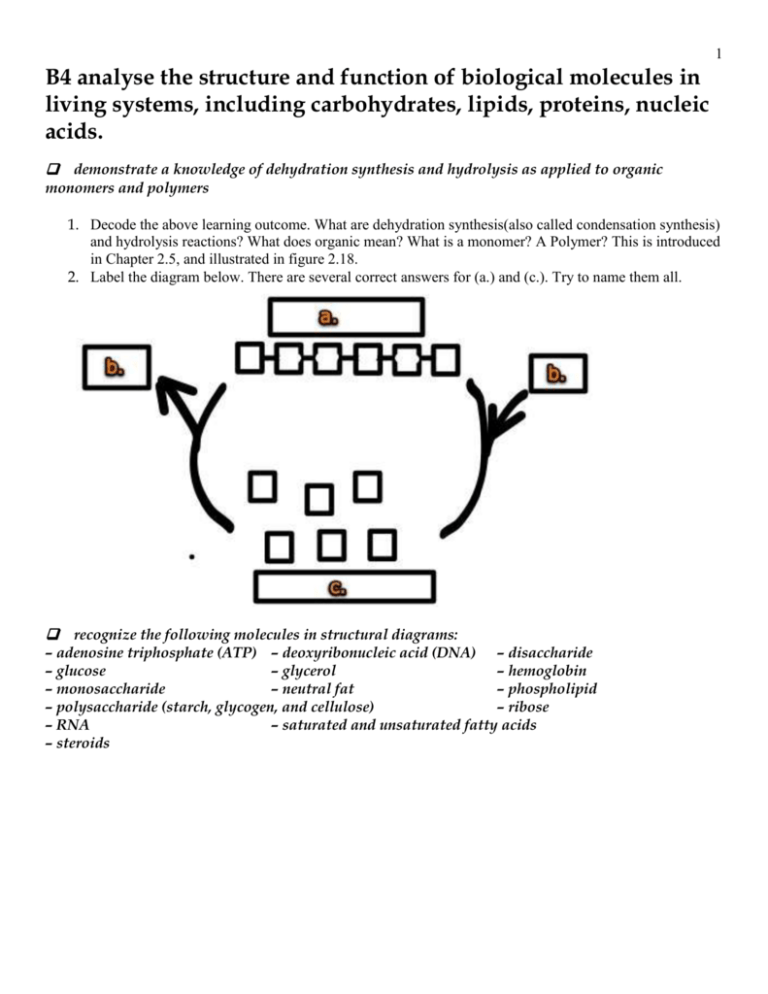
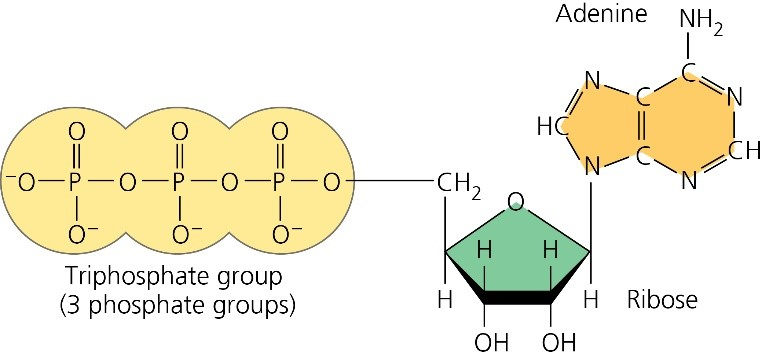
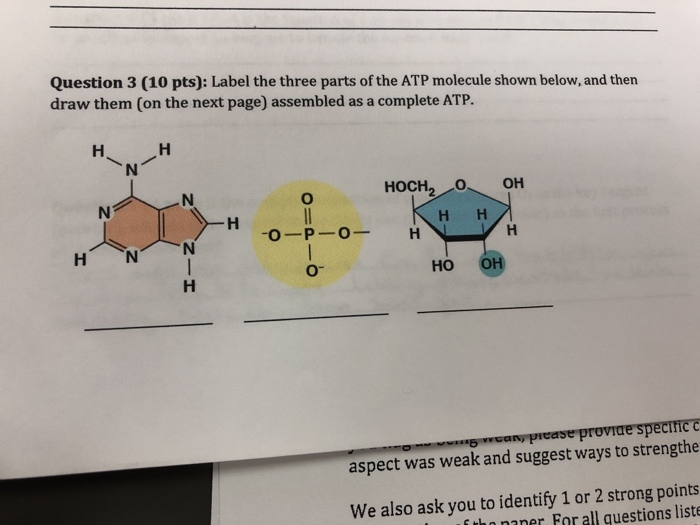
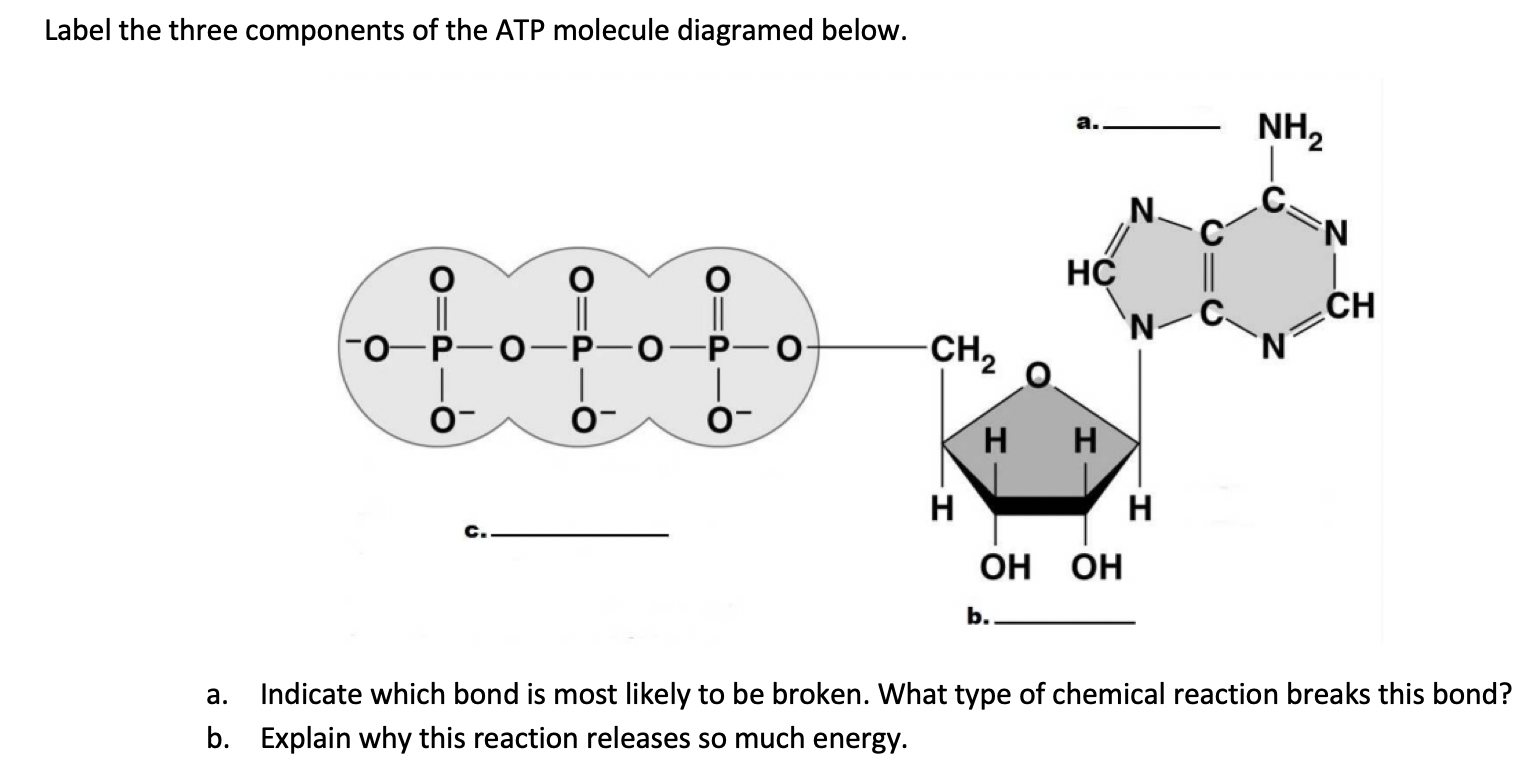
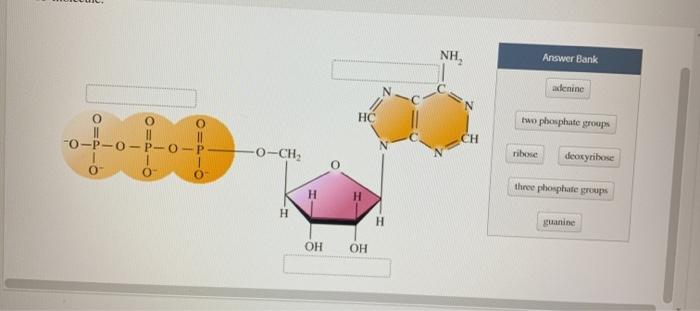
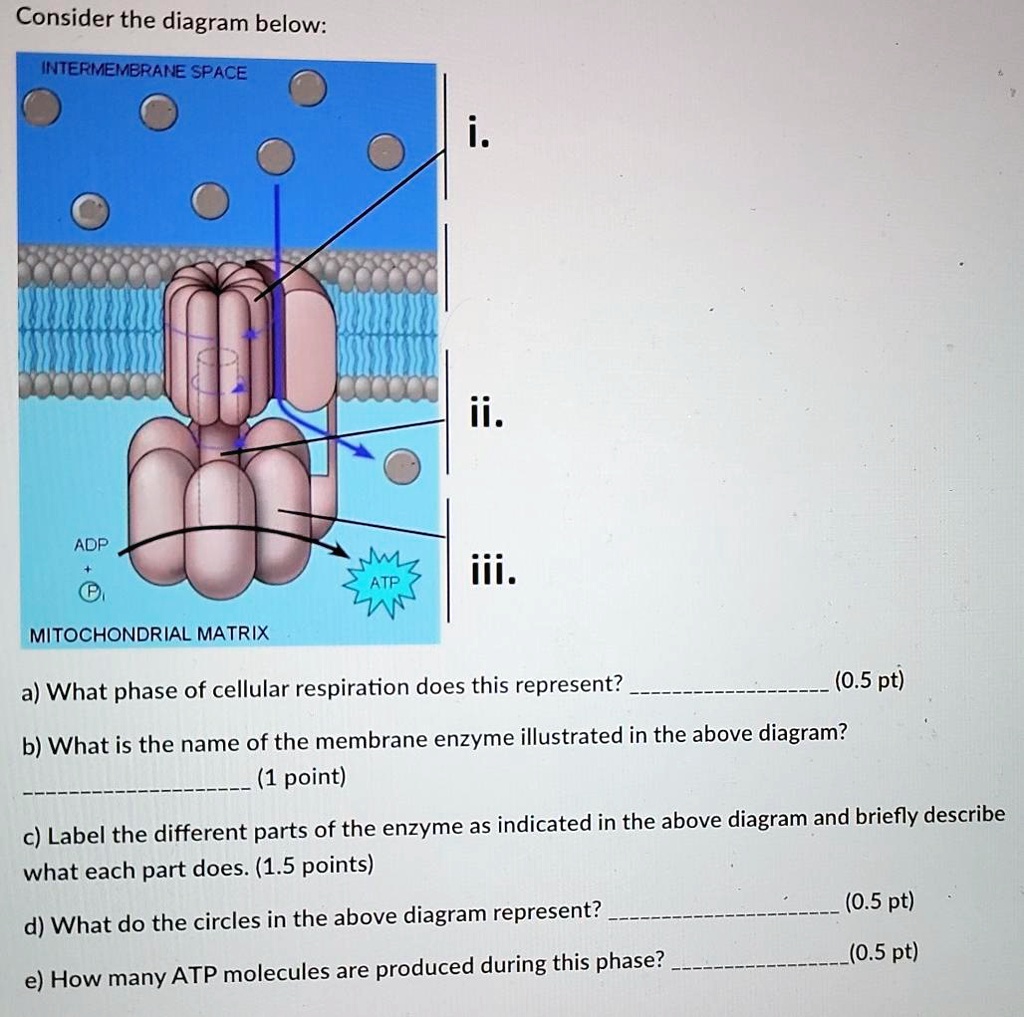
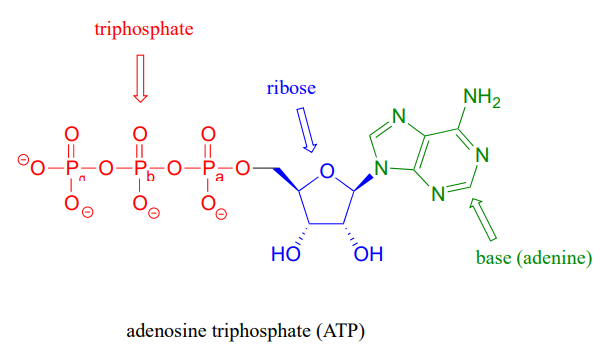
41 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
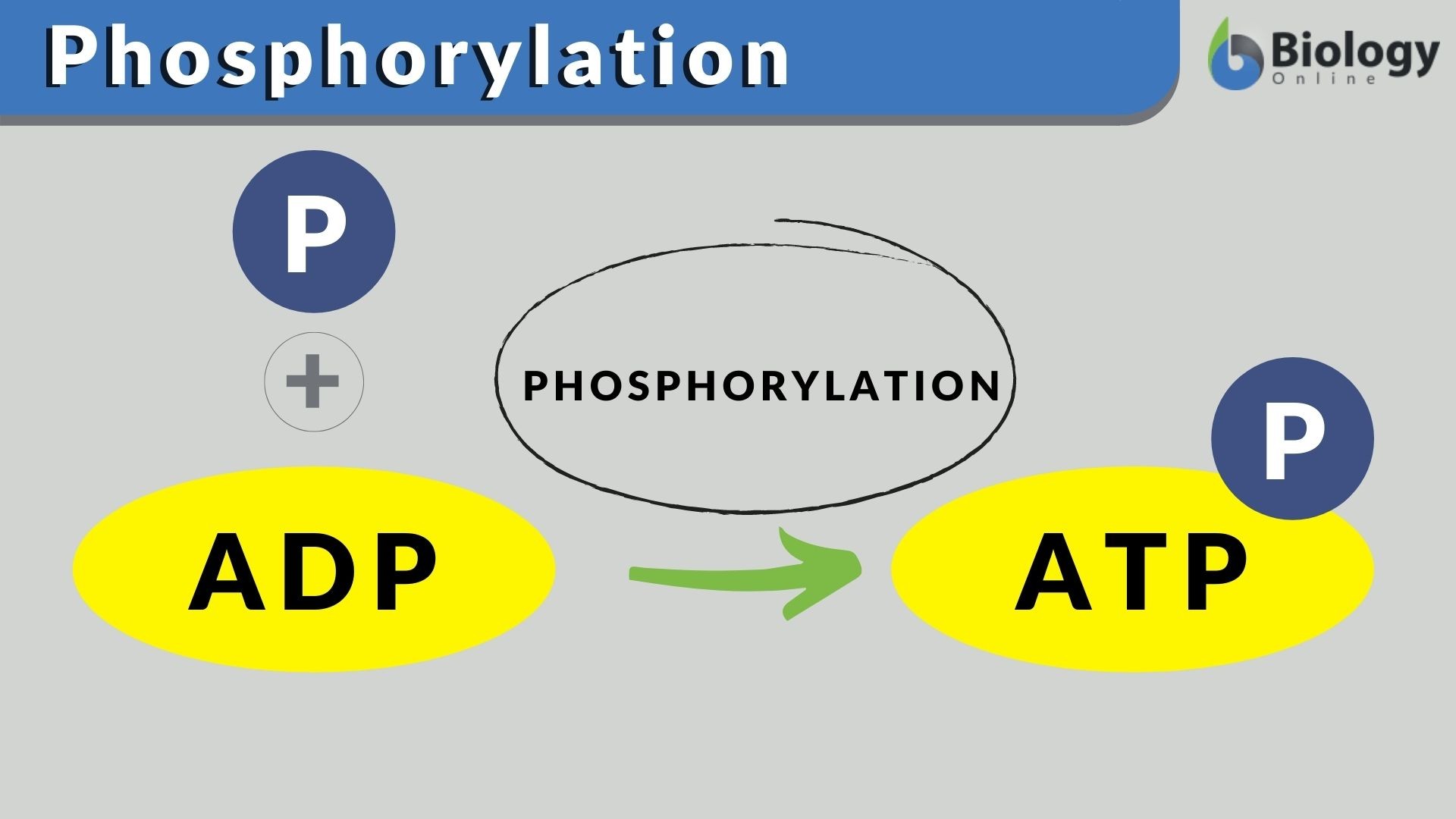
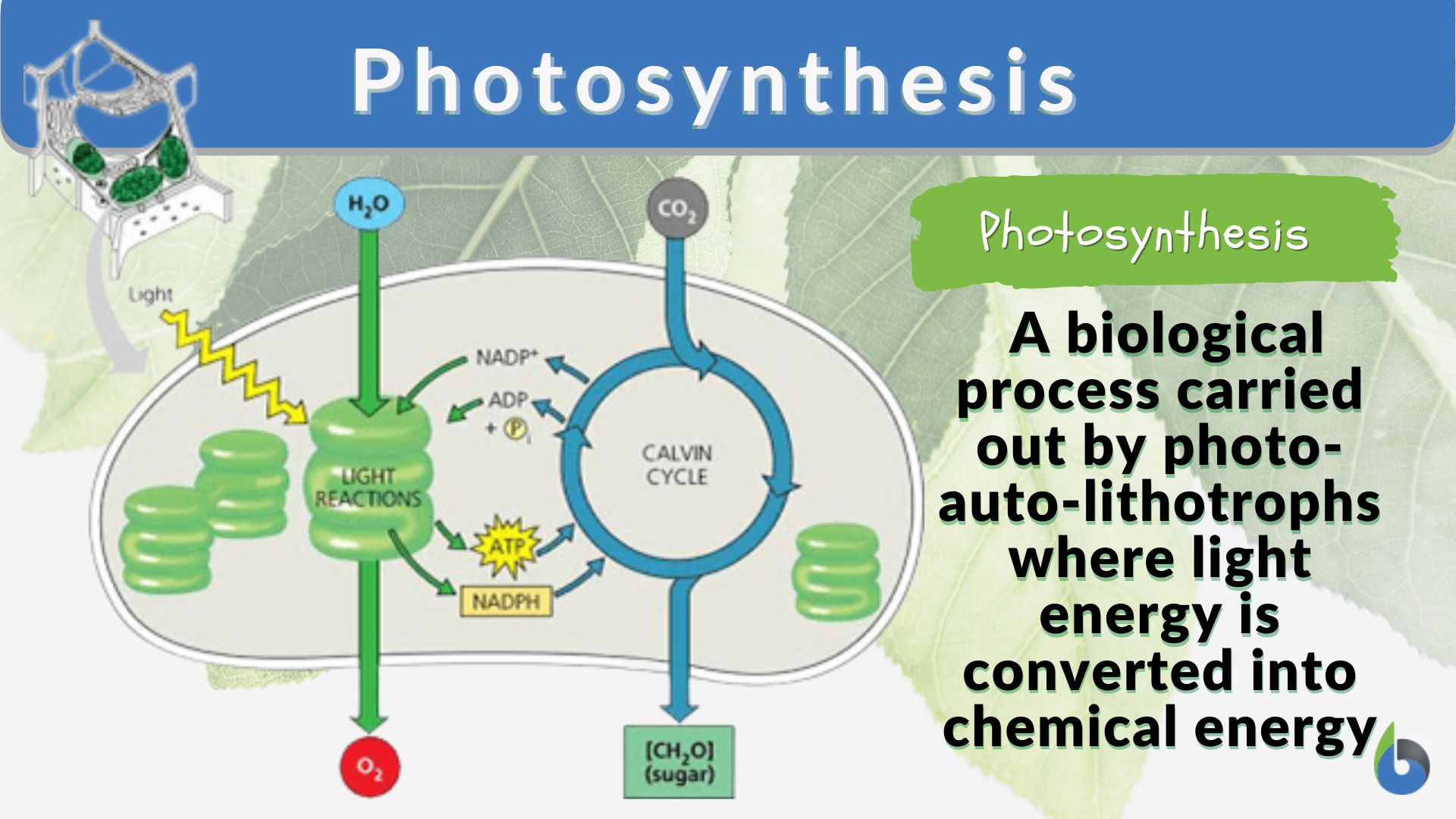
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. 1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.
Chapter 8: Photosynthesis - Paperzz.com ATP has 3 phosphate groups and ADP has 2 phosphates 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Adenosine Ribose Phosphate groups 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? By adding a phosphate group to ADP, producing ATP 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released?
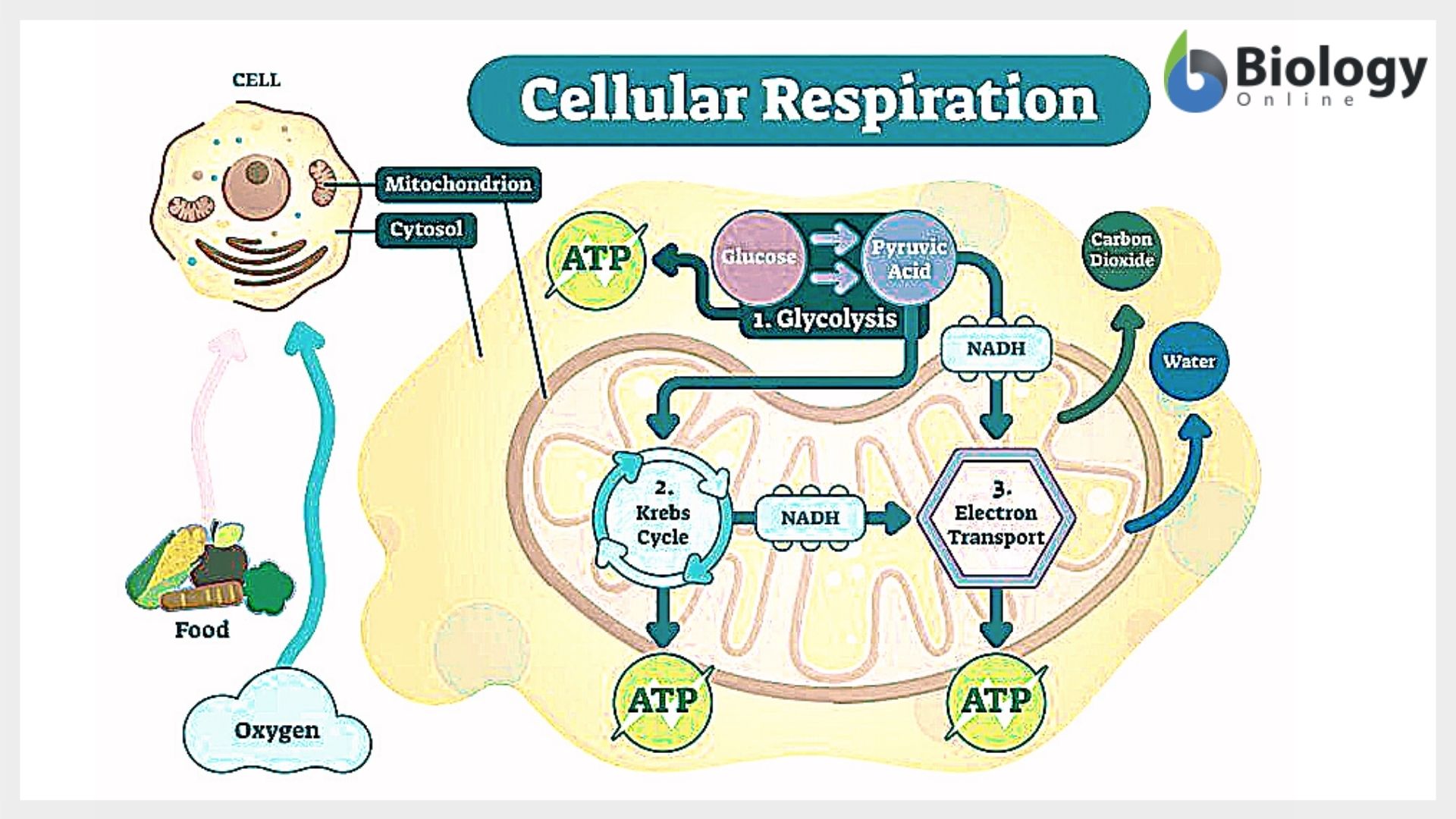
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Cellular-Respiration-58e52b113df78c5162b38dca.jpg)
Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) Chemical Energy and ATP (page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? Bio07_TR_U03_CH08.QXD 4/25/06 2:51 PM Page 63 ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure and hydrolysis. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, SE - Hawthorne High School Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P 6.
Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic 1 Answer Acquaintance Nov 22, 2016 Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: Answer link Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ... What are the three parts of an ATP molecule - Quizlet What are the 3 parts of an ATP molecule adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups Energy is released from ATP when a phosphate is removed Organisms such as plants that make there own food are called autotrophs Plants gather energy with light-absorbing molecules called pigments Most plants appear green because chlorophyll doesn't absorb green light biology honors: chapter 8 Flashcards | Quizlet label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below ... what are the reactants of the photosynthesis reaction? Carbon dioxide and water what are the products of the light-dependent reactions? water and storage where do the light-independent reactions occur? stroma Students also viewed 8.2 photosynthesis 13 terms lauren_ridinger
PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, SE - Hawthorne High School Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P 6. ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure and hydrolysis. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) Chemical Energy and ATP (page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? Bio07_TR_U03_CH08.QXD 4/25/06 2:51 PM Page 63




![Identify the three components [(i),(ii) and (iii)] of ATP ...](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/887889_ba7e3b5cc09d418996079c2f5db4b569.png)














Komentar
Posting Komentar